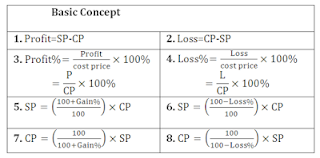
Profit
& Loss
Profit and loss are the terms
related to monetary transactions in trade and business. Whenever a purchased
article is sold, then either profit is earned or loss is incurred.
Cost Price (CP) :This
is the price at which an article is purchased or manufactured.
Selling Price (SP): This is the
price at which an article is sold.
Profit (SP>CP) :When
an article is sold at a price more than its cost price, then profit is earned.
Loss (CP>SP) :When an article is sold at a price lower than
its cost price, then loss in incurred.
Note : Profit and loss always
calculated on cost price.
Some Important Concept
1. If a person sells two similar articles, one at a gain of a% and
another at a loss of a%, then the seller always incurrs a loss which
is given by
Loss%=(a/10)^2 %
2. If a'th part of some items is
sold at x% loss, then required gain per cent in selling rest of the items in
order that there is neither gain nor loss in whole transaction, is (ax)/(1-a)%
Example 1: A medical store owner purchased medicines worth Rs. 6000
form a company. He sold 1/3 part of the medicine at 30% loss. On which gain he
should sell his rest of the medicines, so that he has neither gain or
loss?
Here a = 1/3 , x = 30 %
Required gain % = (1/3*30)/(1-1/3) = 15 %
Here a = 1/3 , x = 30 %
Required gain % = (1/3*30)/(1-1/3) = 15 %
3. If cost price of 'a' articles is equal to the
selling price of 'b' articles, then profit percentage
=(a-b)*100/b
=(a-b)*100/b
4. If a dishonest trader professes to sell his items at CP but
uses false weight, then
Gain %=Error*100/(True Value-Error)
Gain %=Error*100/(True Value-Error)
Gain%=(True weight-False weight)/(False weight)
X100%
Example 2: A dishonest dealer professes to sell his goods at cost price but
he uses a weight of 930 g for 1 kg weight. Find his gain per cent.
Gain % = 70*100/930
Gain % = 70*100/930
5.If a shopkeeper sells his goods at a% loss on
cost price but uses b g instead of c g, then his profit or loss is [(100-a)(c/b)-100]% as sign positive
or negative
Example 3:A dealer sells goods at 6% loss on cost price but uses 14
g instead of 16 g. What is his percentage profit or loss?
Here a = 6 % , b = 14 g and c = 16 g
Required answer = [(100-6)(16/14)-100]% = 7(3/7) %
Here a = 6 % , b = 14 g and c = 16 g
Required answer = [(100-6)(16/14)-100]% = 7(3/7) %
6. If a dealer sells his goods
at a% profit on cost price and uses b% less weight, then his percentage profit
will be
(b+a)/(100-b)X100%
Example 4: A dealer sells his goods at 20% loss on cost price but uses 40%
less weight. What is his percentage profit or loss?
Here a = 20 , b = 40
Required answer = (40 -20)*100/(100- 40) = 33(1/3) %
7. If 'a' part of an article is sold at x% profit/loss, 'b' part
at y% profit/loss and c part at z% profit/loss and finally there is a
profit/lossof Rs.R, then Cost price of entire
article
=RS.(R*100)/(ax+by+cz)
=RS.(R*100)/(ax+by+cz)
Example 5: If 2/3 part of an article is sold at 30% profit, 1/4 part at
16% profit and remaining part at 12% profit and finally, there is a profit of
Rs.75, then find the cost price of the article.
Here a = 2/3 , x = 30 % , b =1/4 , y = 16 % , z = 12 % and R
= 75 Rs
Required CP of article = (75*100)/(2/3*30+1/4*16+1/12*12) = 7500/25 = 300
Required CP of article = (75*100)/(2/3*30+1/4*16+1/12*12) = 7500/25 = 300
1. आदेश ने कुल 25 मॉनिटर और प्रिंटर
ख़रीदे| उसने मॉनिटर का क्रय मूल्य पर 20% चिन्हित किया जबकि प्रत्येक
प्रिंटर को 2000 रुपए का चिन्हित किया| वह 75% मॉनिटर और प्रिंटर का विक्रय
करने और 49000 रुपए लाभ कमाने के लिए सक्षम था| शेष मॉनिटर और 3 प्रिंटर
उसके द्वारा नहीं बेचे जा सकते थे| यदि उसे बिना बेचे गए उत्पाद पर कोई
रिटर्न नहीं मिलता और यह पहले से ज्ञात है कि एक प्रिंटर की कीमत एक मॉनिटर
का 50% है तो उसे पूर्ण से हुई लाभ/हानि ज्ञात कीजिये?
(a) 48,500 रुपए की हानि
(b) 21,000 रुपए की हानि
(c) 41,000 रुपए की हानि
(d) आंकड़ें अपर्याप्त
2. एक रिक्शा डीलर 30 रिक्शा को
4725 रुपए में खरीदता है| उनमें, 8 चार सीटर और शेष दो सीटर हैं| उसे चार
सीटर वाले रिक्शे को कितने मूल्य पर बेचना चाहिए जिससे यदि वह इस मूल्य के
3/4 पर दो सीटर बेचता है तो उसे उसके लागत पर 40% का लाभ प्राप्त हो?
(a) 180 रुपए
(b) 270 रुपए
(c) 360 रुपए
(d) 450 रुपए
(e) इनमें से कोई नहीं
3. रितेश 25 वाशिंग मशीन और माइक्रोवेव ओवन 2,05,000 रुपए में खरीदता है| वह 80% वाशिंग मशीन और 12 माइक्रोवेव 40,000
रुपए के लाभ पर बेच देता है| प्रत्येक वाशिंग मशीन को 20% के अतिरिक्त
मूल्य पर चिन्हित करता है और प्रत्येक माइक्रोवेव ओवन को 2000 रुपए के लाभ
पर बेचता है| शेष वाशिंग मशीन और 3 माइक्रोवेव बेचे नहीं जा सकते| रितेश को
हुई पूरी हानि/लाभ गया कीजिये?
(a)1000 लाभ
(b) 2500 हानि
(c) 1000 हानि
(d) निर्धारित नहीं किया जा सकता
(e) इनमें से कोई नहीं
4. एक फ्लैट और एक जमीन का टुकड़ा
दो मित्रों तरुण और वरुण द्वारा क्रमशः 2 लाख और 2.2 लाख रुपए में ख़रीदा
जाता है| प्रति वर्ष फ्लैट के कीमत में 20% और जमीन की 10% वृद्धि होती
है| दो वर्षों के बाद, वे आपस में अपनी संम्पत्ति बदल लेते हैं| लाभप्राप्तकर्ता का लाभ प्रतिशत लगभग कितना है?
(a) 7.56%
(b) 6.36%
(c) 4.39%
(d) 3.36%
(e) इनमें से कोई नहीं
5. सुनील अपने लाभ प्रतिशत की गणना
विक्रय मूल्य पर करता है जबकि सुजीत अपने लाभ की गणना क्रय मूल्य पर करता
है| वे ज्ञात करते हैं कि उनके लाभ का अंतर 900 रुपए है| यदि उन दोनों का
विक्रय मूल्य एक ही है और सुनील को 50% लाभ प्राप्त होता है और सुजीत को
40% लाभ प्राप्त होता है तो उनका क्रय मूल्य ज्ञात कीजिये?
(a) 4200 रुपए
(b) 4500 रुपए
(c) 4000 रुपए
(d) 4800 रुपए
(e) इनमें से कोई नहीं
6. नमक के मूल्य में 10% की कटौती
एक व्यक्ति को 2 किलो अधिक 180 रुपए में खरीदने के लिए सक्षम करती है| नमक
में हुई कटौती और उसका वास्तविक मूल्य क्रमशः क्या होगा?
(a) 10 रुपए, 9 रुपए
(b) 9 रुपए , 10 रुपए
(c) 18 रुपए, 20 रुपए
(d) 20 रुपए, 18 रुपए
(e) 18 रुपए, 16.2 रुपए
7. एक व्यक्ति पानी घड़ी को 24 रुपए में बेचता है| यदि उसे हुई हानि का प्रतिशत, लागत मूल्य के बराबर है तो घड़ी उसे कितने मूल्य में पड़ी?
(a) 40 रुपए
(b) 60 रुपए
(c) 50 रुपए
(d) 80 रुपए
(e) इनमें से कोई नहीं
8. एक आदमी दो घोड़े 1550 रुपए में
खरीदता है| वह एक 23% हानि और अन्य को 27% लाभ के साथ बेचता है| पूरी
लेनदेन में न उसे लाभ हुआ न हानि| प्रत्येक घोड़े की कीमत क्या है?
(a) 807,743
(b) 817,733
(c) 827,723
(d) 837,713
(e) इनमें से कोई नहीं
9. एक संतरा विक्रेता संतरों को एक निर्धारित मूल्य पर बेचता है और 20%
का लाभ अर्जित करता है| यदि वह प्रत्येक संतरे को 1.2 शुल्क बढ़ा कर बेचता
है तो उसे 40% का लाभ होता है| वास्तविक मूल्य ज्ञात कीजिये जिस पर वे
संतरे बेचता है?
(a) 3 रुपए
(b) 12 रुपए
(c) 4.8 रुपए
(d) 6.0 रुपए
(e) इनमें से कोई नहीं
10. एक घड़ी बेचने के बाद, श्याम को यह पता चलता है कि उस 10% की हानि हुई है| उसे यह भी ज्ञात होता है कि यदि वह उसे 27
रुपए अधिक में बेचता तो उसे 5% का लाभ होता| यदि वह उसे 5% लाभ के साथ
बेचता तो उसे अर्जित हुए लाभ का प्रारंभिक हानि वास्तव में कितना प्रतिशत
था?
(a) 23%
(b) 150%
(c) 200%
(d) 180%
(e) इनमें से कोई नहींउत्तर
1. a
2. b
3. c
4. e (8.189 approx. )
5. a
6. b
7. e (Either Rs 40 or Rs 60)
8. d
9. e (Rs. 3.60)
10. c
To view the above quiz in ENG click herev